

Diabetes / Metabolic Surgery is a type of Weight loss surgery which can be a very effective way of losing weight and putting type 2 diabetes into remission. It involves bypassing or reducing the size of your stomach — so you feel fuller sooner and eat less. Diabetes is one of the major health problems now-a -days affecting large number of populations worldwide. According to World Health Organisation (WHO) by 2025, 300 million people will be suffering from Diabetes. Amongst of all the well known factors that cause diabetes, Obesity is the major risk factor and the most important which has reached epidemic proportion in all the developing countries including India. The increasing onset of diabetes can thus be accredited to the global epidemic of Obesity. Sedentary lifestyle, less physical activity, changing food habits are the major reasons of the substantial increase of this dual epidemic obesity and diabetes. This should be taken as a major concern as this could lead to other fatal conditions like Coronary health disease, cardiovascular disorder, diabetes cardiomyopathy etc…
Diabetes and Obesity are so much interdependent that to describe this a new tern has been coined DIABESITY. As the name explains this term is used to describe the combined adverse health effects of obesity and diabetes mellitus (DM).Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a complex metabolic disease characterized by insulin resistance and progressive failure of pancreas to produce enough insulin resulting in hyperglycaemia. It can be further defined as Metabolic Dysfunction or Metabolic Syndrome caused by decreased ability or total inability of the pancreas to produce insulin which results in Insulin Resistance of Difficulty in secretion of insulin. Both insulin resistance and decreased insulin secretion is seemed very early in the obese patients results in diabetes or worsening it.
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder caused by decreased ability or total inability of the tissues to utilize carbohydrates due to insufficient or inability to produce insulin. The medical management of type 2 DM consists of lifestyle modifications and specific glucose-lowering medications. In few cases this approach is beneficial but when a person has BMI more than 32.5 along with other comorbidities the approach through medication, physical activity & lifestyle changes cannot promise sustained results for “Diabesity”, in that case Bariatric Surgery gives a new life to the person with promising results by curing diabetes and losing weight.
Clinical studies have indicated that circulating bile acid (BA) concentration increases after bariatric surgery, according to it, the increased circulating BA concentrations after bariatric surgery – independently of calorie restriction and body-weight loss – contributes to improve insulin sensitivity, incretin hormone secretion, and postprandial glycemia, leading to the permanent control of type-2 diabetes. The study also shows BA along with gut micro biota also plays a vital role in controlling hyperglycemia condition post-surgery.
After bariatric surgery, patients lose more up to 25% of their total body weight than with any other traditional weight-loss methods. Furthermore, of those with type 2 diabetes, 87% achieve better glucose control and need fewer antidiabetic medications and an average of 78% achieve normal glycaemic control without taking any antidiabetic medications at all. But not all bariatric procedures have the same effect on weight and diabetes certain procedures have a greater effect. The two major types are classified as gastric restrictive procedures and intestinal bypass procedures out of which RYGB(Gastric Bypass) has proven to be a gold standard in weight loss procedures. This procedure combines both restrictive and mal-absorptive elements to limit the size of the stomach and the amount of nutrients and calories absorbed which helps to remit diabetes faster within days even before the patient has lost much weight.
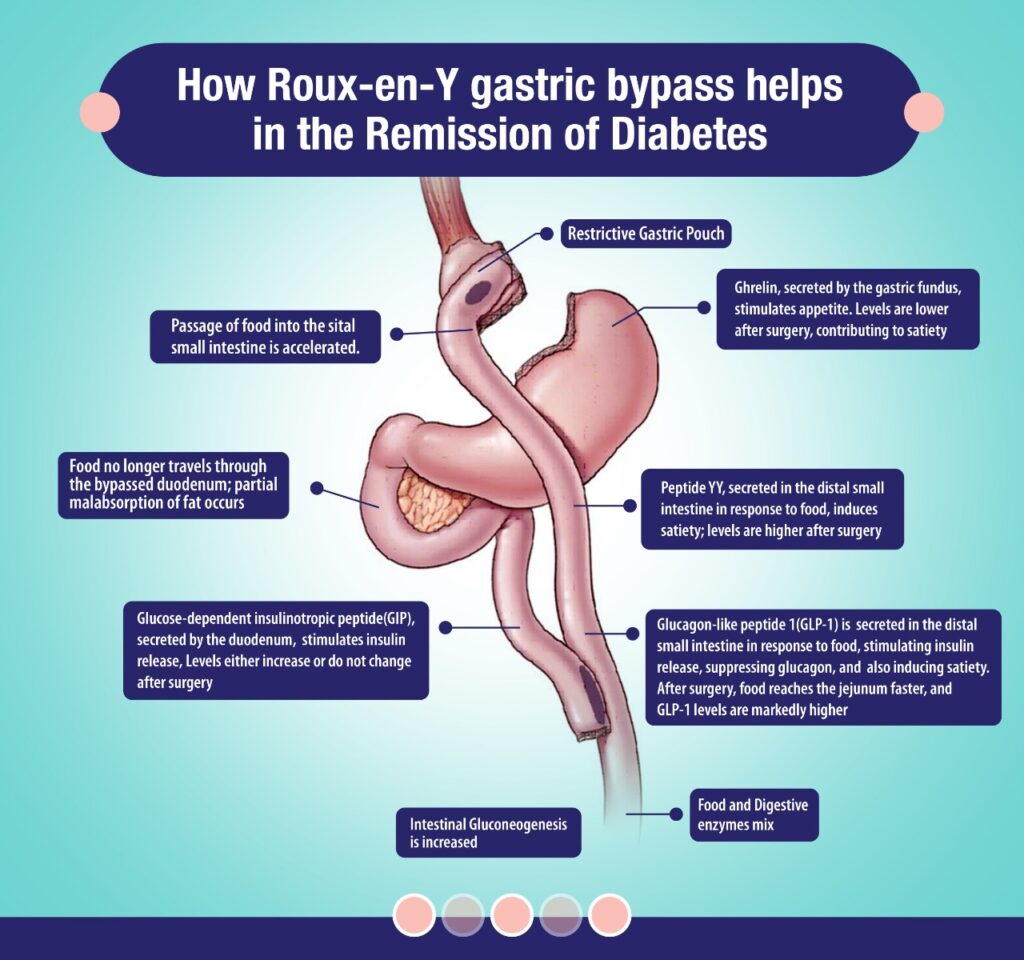
In that case, the major drive for weight loss is the post-operative establishment of a state of profound negative energy balance, leading to the long-term restoration of peripheral insulin sensitivity. The sustained reductions in energy intake post-surgery primarily depends upon the reduction of hunger & early satiety, This is due to either early post-prandial distention of a reduced-capacity of upper gastrointestinal pouch sending satiety signals through the vagal pathways, or to the modulation of hunger and satiety signaling networks in subcortical brain areas regulating energy intake. This mechanism involves post-prandial secretion of satiety-inducing gut peptides such as glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), peptide YY (PYY) and oxyntomodulin (OXM), combined with a diminished secretion of orexigenic hormones such as ghrelin and possibly altered leptin signaling in the hypothalamus & thus help achieving early feeling of fullness. This early satiety need regulation of calorie intake along with medicine or insulin dosage alteration.
According to guidelines from the National Institutes of Health the current indications for bariatric surgery include a BMI of 40 kg/m2 or higher, or a BMI between 35 and 40 kg/m2 with at least two obesity-related comorbidities. Diabetes is considered as a key comorbidity that justifies the risk of surgery. The guidelines suggest that bariatric surgery be offered to all severely obese patients (BMI > 35 kg/m2 ) with type 2 diabetes who have not been able to lose weight with other weight-control approaches. Since type 2 diabetes mellitus is a progressive disease characterized by relentless deterioration of pancreatic beta-cell function, many endocrinologists favour aggressive weight-loss approaches early in the course of the disease. We believe that bariatric surgery should be considered early, as it may help preserve pancreatic beta cell function and slow the progression of any major complications.
One of India’s most highly trained and qualified bariatric surgeons, Dr. Amit Sood combines impressive experience with a deep knowledge of modern surgical techniques and a commitment to achieving the very best outcome for patients.

MBBS , MS , DNB , F GI & HPB , MAS , MARS
Minimal Access , Bariatric , Metabolic and Laparoscopic Surgeon
Dr. Amit Sood, who is the Founder & Director of CKOSMIC HEALTH CITY and his experience forms the core of the organization. He is one of the youngest Minimal Access, Bariatric, Metabolic, Laparoscopic and Endoscopic Surgeon in India and has also been awarded with a Gold Medal in surgery.in surgery.
Best Bariatric Surgeon
Best bariatric surgeon in Punjab
Best bariatric surgeon in Moga
Best bariatric surgeon in Jalandhar
Best bariatric surgeon in Chandigarh
Best bariatric surgeon in Bathinda
Best bariatric surgeon in Amritsar
Best bariatric surgeon in Ferozepur
Best bariatric surgeon in Faridkot
Best bariatric surgeon in Jammu
Best weight loss surgeon
Top Bariatric Weight Loss Surgeon In Ambala
Weight Loss Surgery In Patiala
Best Weight Loss Surgery In Bathinda
Best weight loss surgeon in Moga
Best weight loss surgeon in Ludhiana
Best weight loss surgeon in Jalandhar
Best weight loss surgeon in Chandigarh
Best weight loss surgeon in Bathinda
Best weight loss surgeon in Amritsar
Best weight loss surgeon in Ferozepur
Best Weight Loss Surgery Hospital in Punjab
Important Links
About Dr. Amit Sood – Best Bariatric Surgeon
Contact Us
FAQ’S
Blogs
Ckosmic Health City
G.T. Road, Moga, Punjab, 142001
P. (+91) 73411-01891
P. (+91) 73411-01892
Important Links
About Dr. Amit Sood – Best Bariatric Surgeon
Contact Us
FAQ’S
Blogs
Ckosmic Health City
G.T. Road, Moga, Punjab, 142001
P. (+91) 73411-01891
P. (+91) 73411-01892
Copyright © Designed and Developed By Ckosmic Health City