In India 5% of the country’s total population is suffering with morbid obesity and with this India has moved to 2nd position in the world for the maximum number of obese children after China.Indians aged between 5 and 19 years are increasingly getting obese, according to a report by WHO.It is a well-recognized risk factor for adolescent obesity, which in turn may be the basis of various chronic diseases. So, by preventing the development of obesity in childhood we can reduce the likelihood of obesity in adulthood and its health consequences. The first few complications of obesity to appear are high blood pressure, coronary heart disease and impaired glucose tolerance, diabetes mellitus, joint pain, gout, thyroid, GERD, cancer etc…. will also emerge when not treated on time.
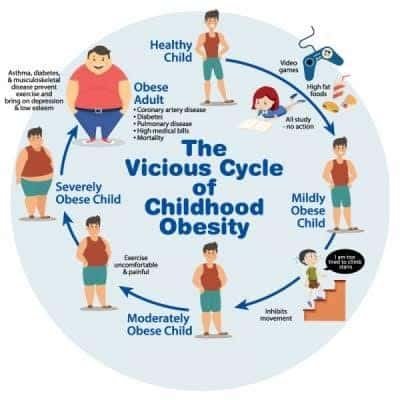
Obesity is a chronic, relapsing and debilitating disease that occurs when a person carries excess weight or body fat. Overweight and obesity result from the interaction of many factors like genetic, metabolic, behavioral, socio-economic and environmental influences. Rapid increase in the obesity levels suggests that behavioral and environmental factors have fueled the epidemic. Sedentary activities in children such as television watching and videogame playing have also increased. Of note, television viewing is associated with greater weight in children and adults, but it is unclear whether this relationship is due more to a corresponding increase in food consumption or a decrease in physical activity. Overall, all these in turn results in weight gain and rapid increase in obesity levels.
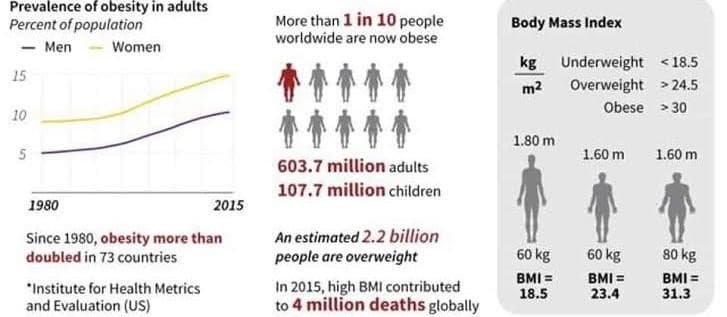
A doctor will usually suggest that a person has obesity if they have a high body mass index. Body mass index (BMI) is a tool that doctors use to assess if a person is at an appropriate weight for their age, sex, and height. BMI measures weight related to height.
A BMI between 18-24.9 is normal; BMI between 25 and 29.9 indicates that a person is carrying excess weight. A BMI of 30 or over suggests that a person may have obesity and a BMI of 32.5 or more with associated comorbidities considered as morbidly obese.
For treating morbid obesity and its associated complications, however, the researchers recommend considering biologically based treatment, including Bariatric/ Metabolic/ Diabetes surgery where appropriate.

